Abiotic Factors In The Forest
Ecosystem Definition
"An ecosystem is defined as a community of lifeforms in concurrence with non-living components, interacting with each other."
Table of Contents
- What is an Ecosystem?
- Structure of the Ecosystem
- Biotic Components
- Abiotic Components
- Types of Ecosystem
- Terrestrial
- Aquatic
- Functions
- Important Ecological Concepts

What is an Ecosystem?
An ecosystem is a structural and functional unit of ecology where the living organisms collaborate with each other and the surrounding environment. In other words, an ecosystem is a chain of interactions between organisms and their environment. The term "Ecosystem" was first coined by A.Grand.Tansley, an English language botanist, in 1935.
Read on to explore the structure, components, types and functions of the ecosystem in the notes provided beneath.
Structure of the Ecosystem
The structure of an ecosystem is characterised by the organisation of both biotic and abiotic components. This includes the distribution of energy in our surround. It also includes the climatic conditions prevailing in that item surround.
The structure of an ecosystem can be divide into ii master components, namely:
- Biotic Components
- Abiotic Components
The biotic and abiotic components are interrelated in an ecosystem. It is an open up organization where the energy and components can flow throughout the boundaries.
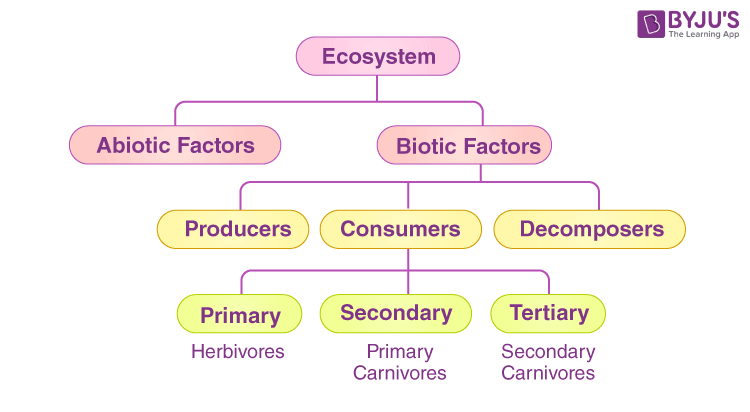
Biotic Components
Biotic components refer to all living components in an ecosystem. Based on nutrition, biotic components can be categorised into autotrophs, heterotrophs and saprotrophs (or decomposers).
- Producers include all autotrophs such as plants. They are called autotrophs every bit they can produce food through the procedure of photosynthesis. Consequently, all other organisms higher up on the food chain rely on producers for food.
- Consumers or heterotrophs are organisms that depend on other organisms for nutrient. Consumers are further classified into primary consumers, secondary consumers and 3rd consumers.
- Principal consumers are always herbivores as they rely on producers for food.
- Secondary consumers depend on primary consumers for energy. They can either be carnivores or omnivores.
- Third consumers are organisms that depend on secondary consumers for food. Tertiary consumers can as well be carnivores or omnivores.
- Fourth consumers are present in some food bondage. These organisms prey on tertiary consumers for energy. Furthermore, they are normally at the meridian of a food chain as they have no natural predators.
- Decomposers include saprophytes such as fungi and bacteria. They directly thrive on the dead and decaying organic matter. Decomposers are essential for the ecosystem as they help in recycling nutrients to be reused by plants.
Abiotic Components
Abiotic components are the not-living component of an ecosystem. Information technology includes air, water, soil, minerals, sunlight, temperature, nutrients, wind, altitude, turbidity, etc.
Functions of Ecosystem
The functions of the ecosystem are as follows:
-
-
It regulates the essential ecological processes, supports life systems and renders stability.
-
Information technology is also responsible for the cycling of nutrients between biotic and abiotic components.
-
It maintains a rest amid the various trophic levels in the ecosystem.
-
It cycles the minerals through the biosphere.
-
The abiotic components help in the synthesis of organic components that involve the exchange of energy.
-
So the functional units of an ecosystem or functional components that piece of work together in an ecosystem are:
- Productivity – Information technology refers to the rate of biomass production.
- Energy flow – It is the sequential procedure through which free energy flows from one trophic level to another. The free energy captured from the sun flows from producers to consumers and then to decomposers and finally back to the environment.
- Decomposition – Information technology is the process of breakdown of expressionless organic material. The peak-soil is the major site for decomposition.
- Food cycling –In an ecosystem nutrients are consumed and recycled dorsum in various forms for the utilisation by various organisms.
Types of Ecosystem
An ecosystem can be as small equally an oasis in a desert, or as big as an body of water, spanning thousands of miles. There are two types of ecosystem:
- Terrestrial Ecosystem
- Aquatic Ecosystem
Terrestrial Ecosystem
Terrestrial ecosystems are exclusively land-based ecosystems. At that place are unlike types of terrestrial ecosystems distributed effectually various geological zones. They are as follows:
- Forest Ecosystem
- Grassland Ecosystem
- Tundra Ecosystem
- Desert Ecosystem
Forest Ecosystem
A woods ecosystem consists of several plants, particularly trees, animals and microorganisms that live in coordination with the abiotic factors of the environment. Forests help in maintaining the temperature of the earth and are the major carbon sink.
Grassland Ecosystem
In a grassland ecosystem, the vegetation is dominated past grasses and herbs. Temperate grasslands and tropical or savanna grasslands are examples of grassland ecosystems.
Tundra Ecosystem
Tundra ecosystems are devoid of copse and are found in common cold climates or where rainfall is scarce. These are covered with snow for almost of the twelvemonth. Tundra type of ecosystem is constitute in the Arctic or mountain tops.
Desert Ecosystem
Deserts are found throughout the world. These are regions with trivial rainfall and deficient vegetation. The days are hot, and the nights are cold.
Aquatic Ecosystem
Aquatic ecosystems are ecosystems present in a body of water. These can be further divided into two types, namely:
- Freshwater Ecosystem
- Marine Ecosystem
Freshwater Ecosystem
The freshwater ecosystem is an aquatic ecosystem that includes lakes, ponds, rivers, streams and wetlands. These have no salt content in contrast with the marine ecosystem.
Marine Ecosystem
The marine ecosystem includes seas and oceans. These have a more than substantial salt content and greater biodiversity in comparison to the freshwater ecosystem.
Also check: Habitat Diverseness

Important Ecological Concepts
1. Nutrient Chain
The sun is the ultimate source of energy on earth. It provides the energy required for all plant life. The plants apply this energy for the process of photosynthesis, which is used to synthesise their nutrient.
During this biological process, light energy is converted into chemical energy and is passed on through successive trophic levels. The flow of energy from a producer, to a consumer and somewhen, to an noon predator or a detritivore is called the food concatenation.
Dead and decaying matter, along with organic debris, is broken downwardly into its constituents by scavengers. The reducers then absorb these constituents. After gaining the energy, the reducers liberate molecules to the environment, which can exist utilised over again past the producers.
2. Ecological Pyramids
An ecological pyramid is the graphical representation of the number, free energy, and biomass of the successive trophic levels of an ecosystem. Charles Elton was the beginning ecologist to describe the ecological pyramid and its principals in 1927.
The biomass, number, and free energy of organisms ranging from the producer level to the consumer level are represented in the form of a pyramid; hence, it is known as the ecological pyramid.
The base of the ecological pyramid comprises the producers, followed by primary and secondary consumers. The third consumers hold the apex. In some nutrient chains, the quaternary consumers are at the very apex of the food chain.
The producers generally outnumber the primary consumers and similarly, the primary consumers outnumber the secondary consumers. And lastly, noon predators also follow the same trend every bit the other consumers; wherein, their numbers are considerably lower than the secondary consumers.
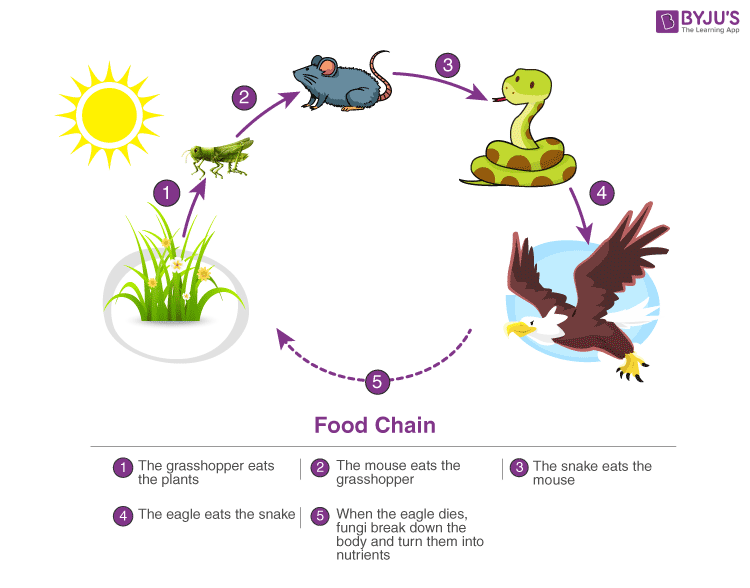
For instance, Grasshoppers feed on crops such as cotton and wheat, which are plentiful. These grasshoppers are then preyed upon by common mouse, which are insufficiently less in number. The mice are preyed upon by snakes such as cobras. Snakes are ultimately preyed on by apex predators such as the brown snake eagle.
In essence:
Grasshopper →Mouse→ Cobra → Dark-brown Snake Hawkeye
three. Food Web
Food web is a network of interconnected food chains. Information technology comprises all the food chains within a unmarried ecosystem. It helps in understanding that plants lay the foundation of all the food chains. In a marine environment, phytoplankton forms the principal producer.
Main article: Food spider web
To learn more than about what is an ecosystem, its structure, types, components, and functions, register at BYJU'S website or download the BYJU'South app.

Frequently Asked Questions
i. What is the ecosystem?
The ecosystem is the community of living organisms in conjunction with non-living components of their environment, interacting equally a system.
2. What are the different types of ecosystems?
The dissimilar types of the ecosystem include:
- Terrestrial ecosystem
- Wood ecosystem
- Grassland ecosystem
- Desert ecosystem
- Tundra ecosystem
- Aquatic ecosystem
- Freshwater ecosystem
- Marine ecosystem
3. What are the functional components of an ecosystem?
The iv chief components of an ecosystem are:
(i) Productivity
(ii) Decomposition
(iii) Free energy menses
(4) Nutrient cycling
iv. Which ecosystem practice we live in?
We live in a terrestrial ecosystem. This is the ecosystem where organisms collaborate on landforms. Examples of terrestrial ecosystems include tundra, taigas, and tropical rainforests. Deserts, grasslands and temperate deciduous forests also plant terrestrial ecosystems.
5. What is the structure of the ecosystem?
The structure of the ecosystem includes the organisms and physical features of the environment, including the amount and distribution of nutrients in a particular habitat. Information technology likewise provides data regarding the climatic conditions of that expanse.
6. Which is the largest ecosystem in the world?
The largest ecosystem in the world is the aquatic ecosystem. Information technology comprises freshwater and marine ecosystems. It constitutes lxx% of the surface of the world.
7. What is the major part of an ecosystem?
The ecosystem is the functional unit of the environment system. The abiotic components provide the matrix for the synthesis of organic components. This process involves the commutation of energy.
8. What makes a good ecosystem?
A good ecosystem consists of native plants and animal species interacting with each other and the environment. A healthy ecosystem has an energy source and the decomposers that suspension down dead plants and animal matter, returning essential nutrients to the soil.
ix. What all include the not-living things in an ecosystem?
The non-living things in an ecosystem include air, wind, h2o, rocks, soil, temperature and sunlight. These are known as the abiotic factors of an ecosystem.
Register at BYJU'S for ecosystem notes or other of import study resources.
Further Reading:
- Our Environs
- Free energy Menstruum In Ecosystem
- What Is A Natural Ecosystem?
- Why Is The Ecosystem Important?
- What Are The Five Levels Of Ecology?
- What Are The Dissimilar Fields Of Ecology?
- What Are The Three Environmental Issues?
- Difference Between Food Chain And Food Web
- How Many Types Of The Ecosystem Are At that place?
- How Tin can We Improve Our Environmental Health?
Abiotic Factors In The Forest,
Source: https://byjus.com/biology/ecosystem/
Posted by: tierneywevere.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Abiotic Factors In The Forest"
Post a Comment